Prerequisites
Before you start building your Data Lakehouse, make sure you have the following prerequisites:- A Datazone account. If you don’t have one, you can sign up here.
- Datazone CLI installed on your local machine. You can install it by following the instructions here.
Task List
To understand how to build a Data Lakehouse from scratch using Datazone, let’s follow these steps:- 🔌 Connecting your data source: Start by connecting AWS S3 as a data source.
- 📁 Initialize first project: Set up your first project and add an Extract component.
- 🚀 Run first execution: Launch your first execution to fetch data from the source.
- 📄 Create first pipeline: Design a simple pipeline to process the data.
- 🚂 Run first pipeline: Execute the pipeline to transform your data.
- ⏰ Create first schedule: Configure periodic runs for automated processing.
- 🧠 Create an Intelligent App: Turn your data pipelines into context-aware applications that observe, reason, and act — not just visualize.
- 🤖 Deploy an Agent: Set up AI-powered automation for monitoring and insights.
- 🔗 Expose data via Endpoints: Create secure APIs for your processed data.
- 🏆 Access the data: Learn how to query and use the processed data.
🔌 Connect Source
1.Go to Settings from the top-right user menu, then select Sources under the Integrations section.
- Click on the Create Source button.

- Fill in the required fields and click on the Create button. And you are done! You have successfully connected your source. Check your source in the Settings > Sources page.

📁 Create Project
- Go to the Projects page by clicking on the Projects tab in the sidebar.

- Click on the Create Project button.

- Fill in the required fields and click on the Create button. Boom! 🚀 You have successfully created your first project.

Define your Extract
- On your project page, click on the Add button in the top right corner to add a new entity.
- Select Extract as the entity type.

- Fill in the required fields and click on the Create button. You have successfully created your first Extract entity.

-
name: The name of the extract. -
source: The source you want to extract data from. (It is already selected) -
mode: The mode of the extract. Options are;-
Overwrite: Fetch all the data from the source every time. -
Append: Fetch only the new data from the source.
-
-
search_prefix: The prefix you want to search for in the bucket. -
search_pattern: The pattern you want to search for in the bucket.
🚀 Run First Execution and Check the Data
- Click to the created Extract entity and move to the Executions tab. Via clicking the Run button, you can start your first execution.

- Simultaneously, you can check the execution logs and the other details in the Logs tab. You can cancel the execution if you want. After a while, execution will be completed and you notice the new dataset in left explorer. You can check the data by clicking on the dataset.

- On the dataset drawer, you can see the data fetched from the source. You can also check the schema and make queries on the data to explore it.

- With above way, we can fetch the other csv files from the source and create the datasets for each of them.
⌨️ Click Less, Code More: Create First Pipeline
If you have already created your project on the UI, open the project page and move to the “Code” section in the left tabs. For local development, clone it using the Datazone CLI.- We can create our pipeline file in the project folder. Let’s create a new file named
order_reports.pyin the project folder.
order_reports.py
-
You can see that we have two functions that are decorated with
@transform. These functions are the steps of the pipeline. You can specify the input datasets and the output dataset of the function by using theinput_mappingandoutput_mappingclasses. -
The first function
join_tablesjoins theorders,order_lines, andcustomerstables. -
The second function
sales_by_countrycalculates the total sales and order count by country. -
The third function
most_popular_productscalculates the total sales, total quantity, average price, and order count by product.
- Then you need to reference this pipeline in the
config.ymlfile.
config.yml
- Write your code in the “Code” section of the project page and click the Deploy button.

- Click the Execute button in the pipeline page.
There are many ways to do something in Datazone. You can run your pipeline via
UI, CLI or API.
- While execution is running, you can check the logs both in the terminal and in the UI. After the execution is completed, you can check the logs and the output dataset in the Executions tab.

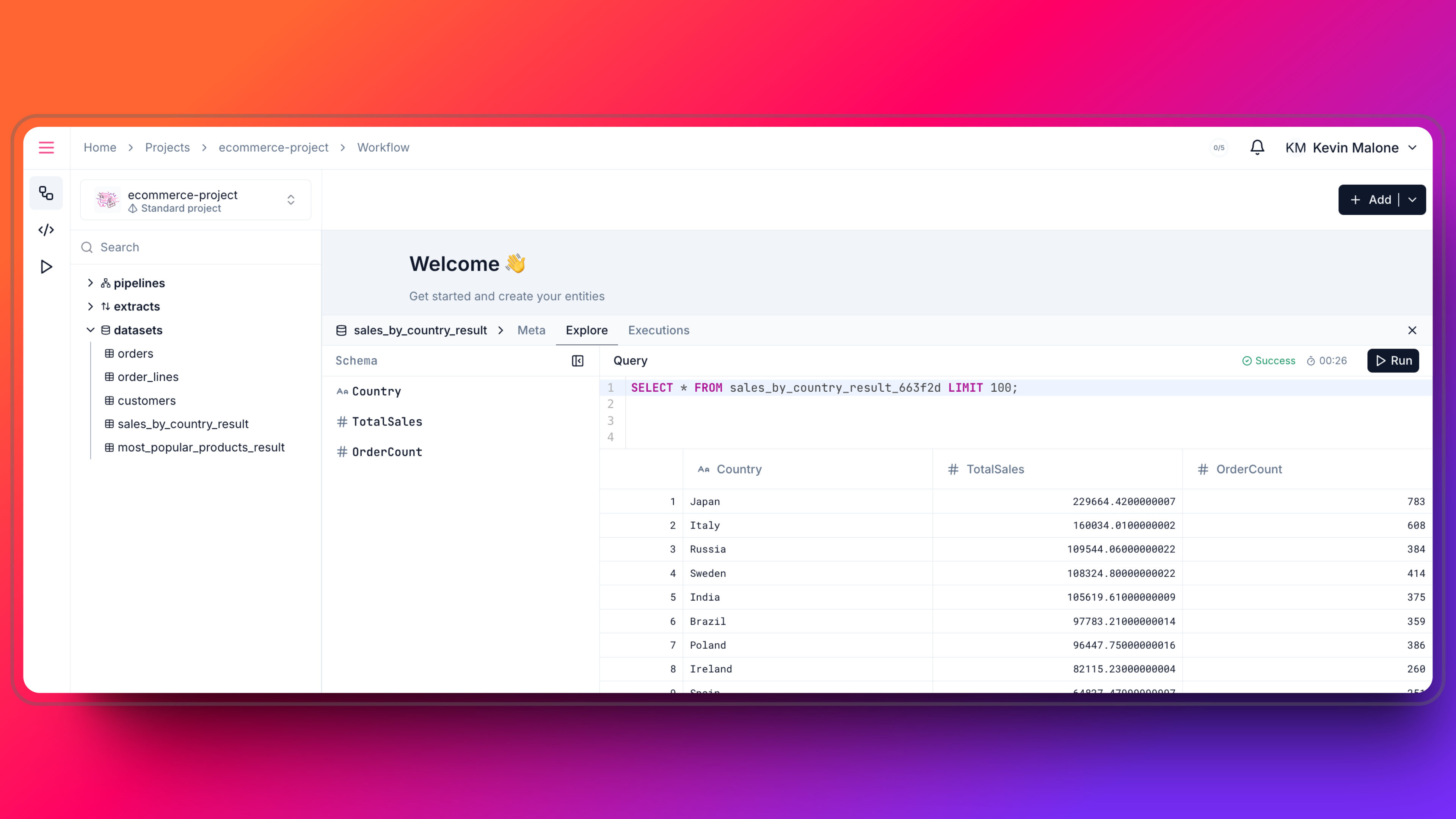
- Our new Dataset is ready to use. You can check and explore the data in the dataset drawer.
⏰ Orchestrate Your Pipeline
- Select the pipeline you want to schedule in the Explorer.
- Open the Schedules tab and click on the + Set Schedule button.
-
Attributes are:
-
pipeline: The pipeline you want to schedule. (It is already selected) -
name: The name of the schedule. -
expression: The cron expression for the schedule. You can use the presets or write your own.
-

🧠 Create an Intelligent App
At this point, your pipelines are producing reliable and structured datasets. In Datazone, an Intelligent App is built on top of these pipelines to turn data into context-aware applications. An Intelligent App can:- Observe changes in datasets over time
- Understand relationships between entities
- Surface meaningful insights without manual queries
🤖 Deploy an Agent
Agents bring automation and intelligence into your Datazone applications. An Agent continuously monitors selected datasets, pipelines, or executions and reacts based on context. Typical use cases include:- Detecting anomalies in data or execution behavior
- Monitoring pipeline health and failures
- Identifying unusual trends or patterns
- Providing proactive insights without user interaction
🔗 Expose Data via Endpoints
After processing and enriching your data, you can expose it using Endpoints. Endpoints allow external applications and services to securely access your datasets via APIs. Key benefits:- Secure access using API keys
- Controlled exposure at dataset or view level
- No direct database access required